The components of male leather shoe
Have you ever felt embarrassed when buying a pair of men's shoes and sellers used English terms that you could not understand to introduce shoes? Or have you ever been interested in learning about the structure of your shoes that you wear daily? The article below will help you become a fashion expert in the footwear field right away.
Overview of men's leather shoe structure
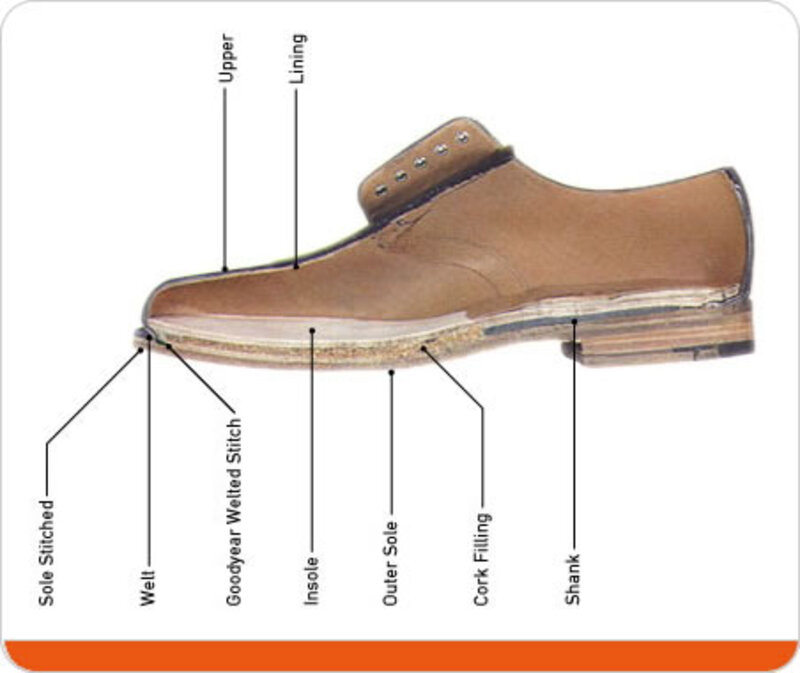
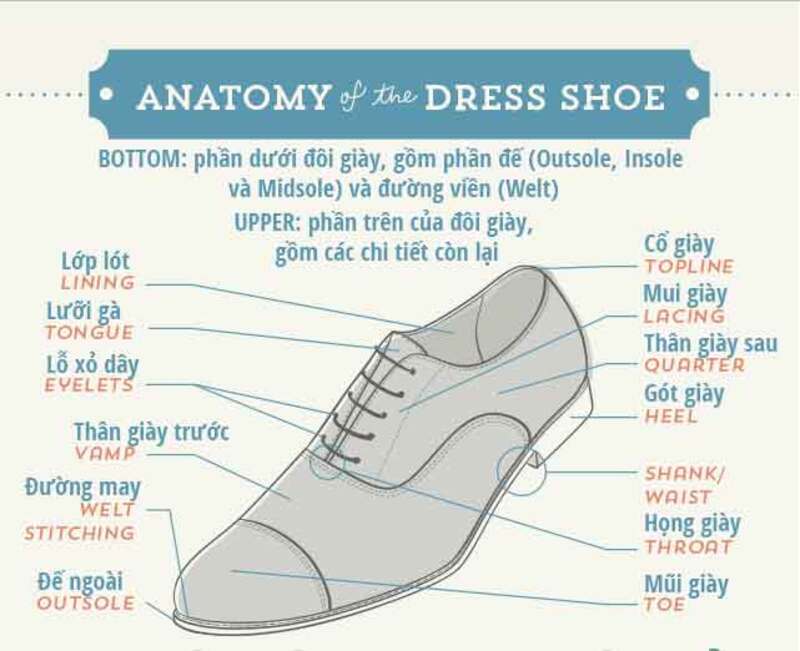
In general, a shoe is divided into two main parts: upper and sole. Upper is the name of the entire cover of the foot and does not touch the ground. We call it the familiar name "shoe's surface". Sole is the part bearing the foot and directly contacts with the ground.
Details of the components making up a pair of leather shoes
For details, a pair of high-end men's shoes include to 20 different parts from tiny shoelace to shoesole. They all are considered as important components to create a pair of shoes. .
Components of shoe's upper
Toe cap: helps protect the carrier's toes. For high-end men's leather shoes, toe cap is one of the important parts increasing or decreasing the formality of the shoes.
Vamp: from the behind of shoetoe to around the eyelet, tongue and quarter.
Quarter (hindquarters of the shoe): hugging the foot.
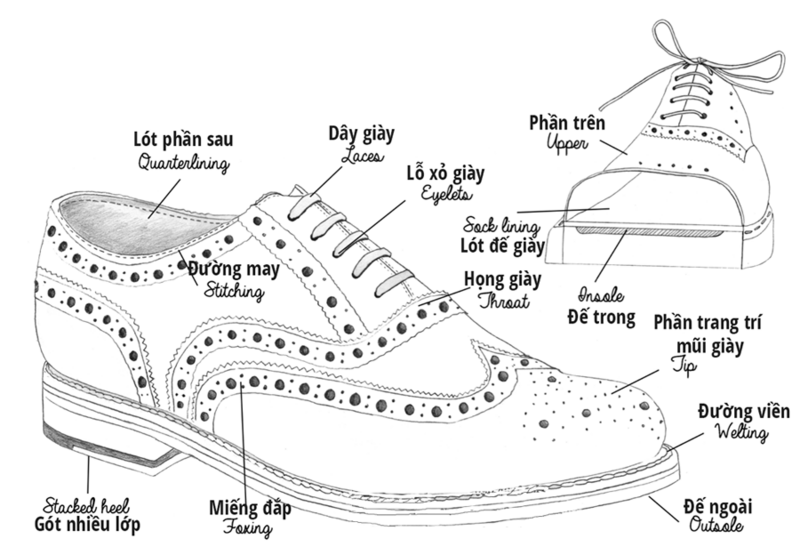
Eyelet: a hole punched through the shoe leather and covered with two metal, plastic or rubber. Both of them are responsible for holding firmly for the hole and prevent the hole from being torn.
Eyestay: The material section contains the piercing holes
Laces: These allow you to pierce and tie the shoelaces through the piercing holes to help hold two sides of shoe together.
Tongue: The cushion between the shoe vamp and instep. Tongue protects the opened lacing part and avoids friction between instep and the shoe.
Lining: acts as a gentle contact with foor and give a dry feel to the shoe.
Collar: feeling of wideness, tightness at ankle will originate from this part of the shoe.
Topline: The highest part of the shoe neck.
Heel counter: Besides heel protection, the heel counter also helps to shape the heel of the shoe. Heel counter has reinforced material made of hard plastic (TPU/TPR) or thermo-sheet.
Throat: is the junction between the shoelaces and the vamp
Socklining/sock liner. Socklining is used as a cushion for increased comfort when wearing shoes, it removes foot odor and sweats to increase shoe stability. Socklining can also be replaced easily.
Stitching: Stitching the pieces of leather material together.
Welt: It can be a leather or synthetic material that is located in the opened part between the upper and the sole, in the edge of the shoe sole.
Components of shoe sole
Sole is divided into three main categories:
Insole: Located in the inside of the shoe, below the foot, under shoelining, in direct contact with the person's foot. Insole helps to adjust the shape of the shoe and increase comfort when using.
Midsole: The pad between the insole and the outsole. This is a part of the cushioning function for carriers on the move.
Outsole: is a layer of material that is in direct contact with the ground. Outsole can be a original piece or be assembled from various pieces with different material. This part is the most abraded part due to the role of friction resistance for the carrier to move easily.
Depending on the structure and purpose of each type of shoes, the midsole and outsole will have different thicknesses and designs. Men's western shoes will not focus on the midsole.
There is also a shank (often referred to as "shoe backbone") that helps stabilize the arch and when moving. Shank on western shoe is usually made of metal.
Men's leather shoes are extremely complex, so it's not easy to make a pair of western shoes. Footwear manufacturers have to invest not only in modern technology but also the effort to produce the highest quality shoes. And of course, the effort they put out has always been welcomed by fashion fans including the famous brands such as Oxford, Clarks, Banuli, Cole Haan ... Currently, in Ho Chi Minh, there was a shoe factory of Banuli at 64/3L, Dong Tam street, My Hoa 3 hamlet, Tan Xuan commune, Hoc Mon district, HCMC. Or, if you do not have access to the workshop, you can contact 0915 129 579 or 0967 696 769.